-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 404
AWS IAM
Note: This feature is available in Enterprise, AWS, Team editions only.
CloudBeaver supports AWS IAM authentication to enhance security for database operations within AWS environments.
This guide details the configuration process for AWS IAM authentication, applicable to all CloudBeaver versions, with an emphasis on the initial setup required for the AWS version.
For comprehensive setup information of AWS IAM itself, refer to the official AWS IAM documentation.
-
As an administrator, go to Settings -> Server Configuration.
-
Find the AWS option (in the Configuration section) and AWS IAM (in the Authentication Settings section). Activate this setting to enable AWS authentication.

-
Save the changes.
For instructions on configuring AWS Regions, see AWS Settings.
-
As an administrator, navigate to Settings -> Identity Providers.
-
Click on the + Add button.
-
Fill in the following fields:
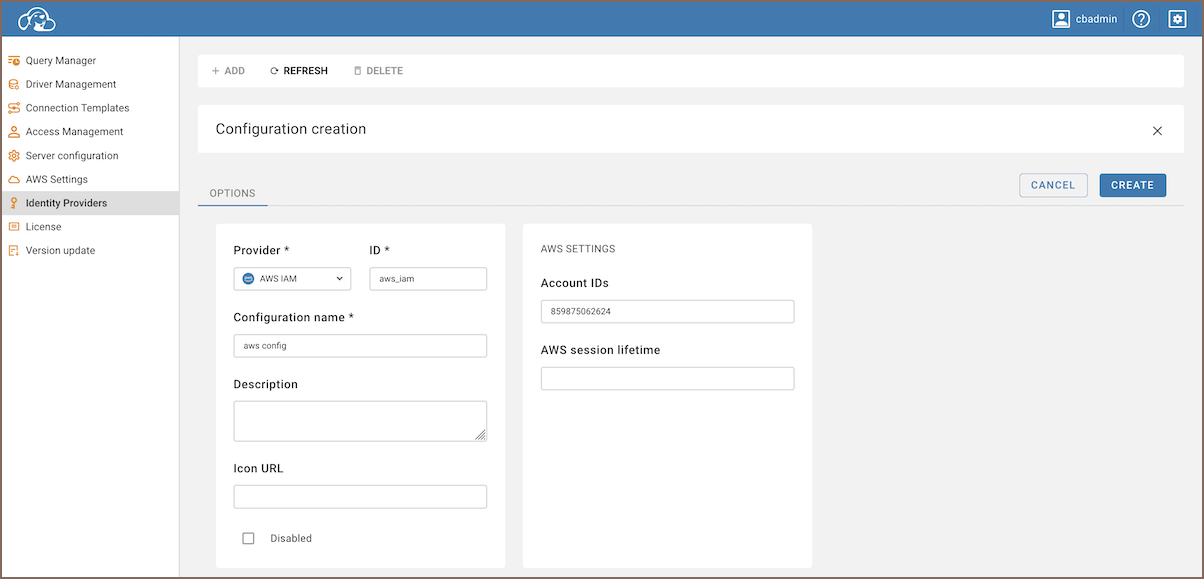
Field Description Provider Select AWS IAMfrom the dropdown menu.ID Enter a unique identifier for the configuration. Configuration name Enter a descriptive name for this configuration. Description Provide a brief description of this identity provider configuration. Icon URL Enter the URL of an icon to represent this provider. Disabled Leave unchecked to enable this identity provider. Account IDs Enter AWS Account IDs, separated by commas. Only users from these accounts are allowed. AWS session lifetime Specify the duration for the AWS session in seconds.
Tip for Account IDs: You can create entries for different Identity Providers for a more flexible configuration.
- Click on the Create button.
-
With the AWS configuration now established, proceed to the login screen.
-
You will be presented with two options for key types:
- For permanent credentials, select
Static access keys. - If using credentials that change regularly, select
Temporary access keys.
- For permanent credentials, select
-
Input your
Access KeyandSecret Keyin the respective fields.- If you selected
Temporary access keys, enter yourSession Tokenin the additional field that appears.
- If you selected
-
Confirm your details and click the
LOGINbutton to authenticate.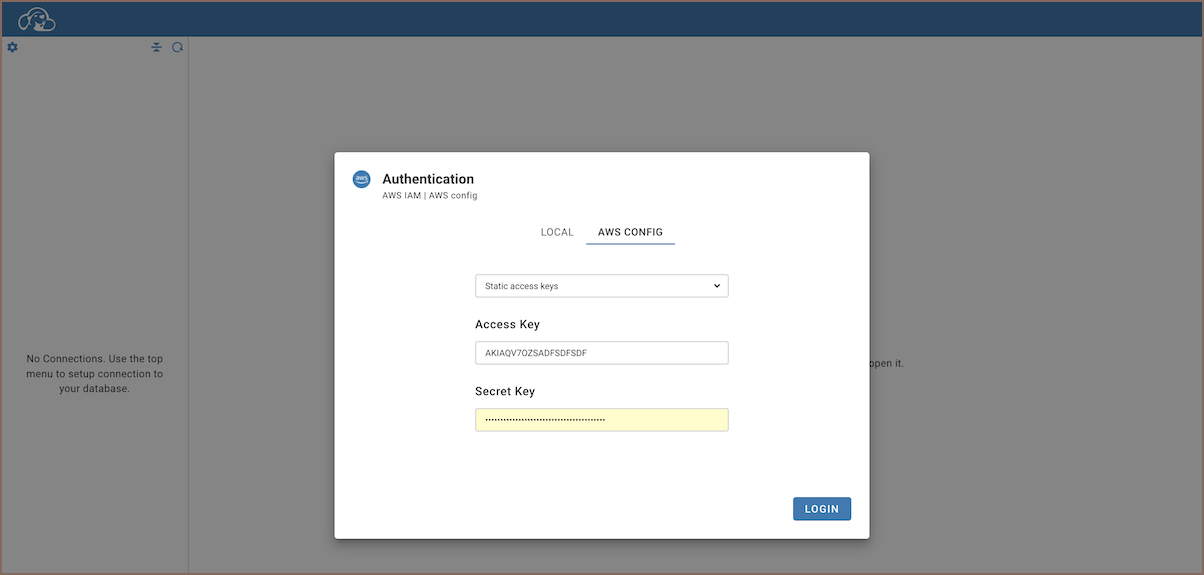
Note: To make databases available for users who log in via AWS IAM, the administrator must first add the desired databases. This is done by navigating to Connections -> Cloud Connections and including them in the Database Navigator.
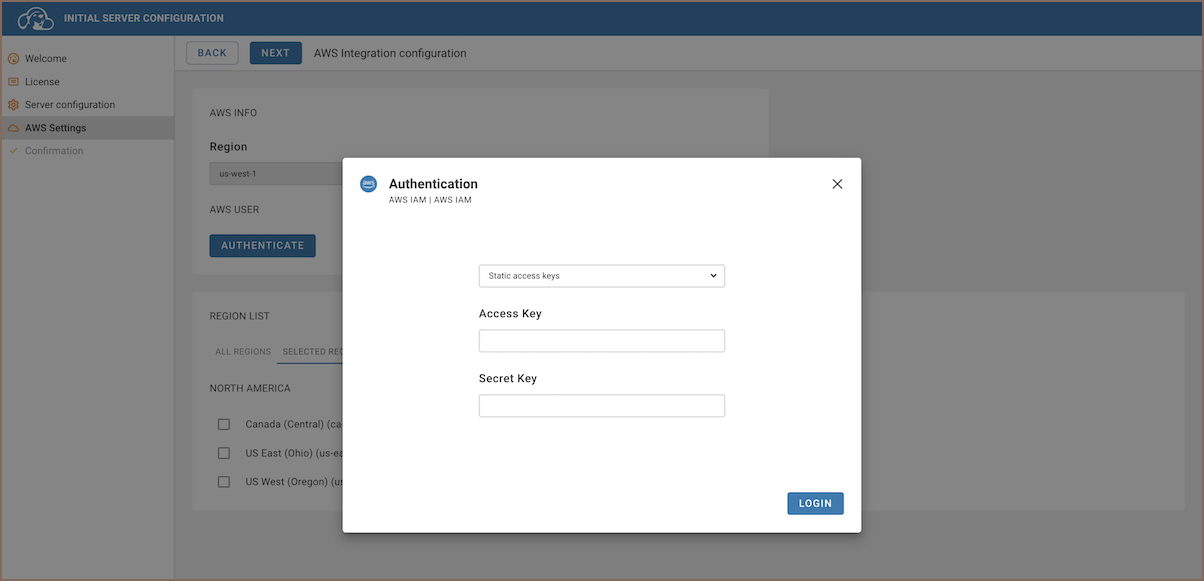
When configuring the CloudBeaver AWS Edition for the first time, AWS IAM credentials are mandatory. This version is optimized for the AWS Marketplace and specifically requires IAM authentication to integrate with AWS services.
During the initial launch, you are required to input your IAM user's Access Key ID and Secret Access Key to establish the necessary AWS integrations.
-
No Server-Side Key Storage: CloudBeaver is designed not to store AWS access and secret keys on the server, ensuring they are not held in databases or configuration files. This approach is crucial for maintaining the security of your data.
-
Automatic administrator role assignment: The AWS user responsible for configuring CloudBeaver automatically receives administrator privileges in the CloudBeaver instance. This user will have comprehensive control over the instance's settings and configurations.
-
AWS account association: Upon completing the server configuration, the AWS account of the administrator is associated with the CloudBeaver instance. This means that only AWS users belonging to this specific account can authenticate and access this instance of CloudBeaver.
-
User management within AWS scope: CloudBeaver for AWS does not support the creation of new users within its platform. It solely operates with existing AWS user accounts. Consequently, every user who needs access must authenticate through their AWS account.
-
Database Authentication Requirements: AWS databases typically have their own authorization mechanisms, requiring additional authentication parameters such as a username and password. For RDS/Aurora databases using IAM authentication, you may only need to provide the database username, leaving the password field empty.
CloudBeaver uses the following AWS services in order to operate with databases (most of them are optional):
- STS (required): used for user authentication
- RDS: list RDS/Aurora instances for cloud databases explorer (describeDBInstances)
- Redshift: list Redshift clusters for cloud databases explorer (describeClusters)
- DynamoDB: all DynamoDB services for DynamoDB operating. Can be read-only for read-only DynamoDB access.
- DocumentDB: list DocumentDB clusters for cloud databases explorer (describeDBClusters)
- IAM (optional): additional user/organization information read (like account organization name)
CloudBeaver uses native database clients to connect and operate with most databases. It uses AWS services only to find database instances and configure database connection.
The only exception is the DynamoDB service which is a database driver by itself. You can limit DynamoDB access directly in the AWS console.
- Application overview
- Demo Server
- Administration
- Server configuration
- Create Connection
- Connection Templates Management
- Access Management
-
Authentication methods
-
Local Access Authentication

- Anonymous Access Configuration
- Reverse proxy header authentication
- LDAP
-
Single Sign On

-
SAML

-
OpenID

-
AWS OpenID

-
AWS SAML

-
AWS IAM

-
AWS OpenId via Okta

-
Snowflake SSO

-
Okta OpenId

-
Cognito OpenId

-
JWT authentication

-
Kerberos authentication

-
NTLM

-
Microsoft Entra ID authentication

-
Google authentication

-
Local Access Authentication
- User credentials storage
-
Cloud Explorer

-
Cloud storage

-
Query Manager

-
Drivers Management

- Supported databases
- Accessibility
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Features
- Server configuration
- CloudBeaver and Nginx
-
Domain manager

- Configuring HTTPS for Jetty server
- Product configuration parameters
- Command line parameters
- Local Preferences
- API
-
CloudBeaver Community
-
CloudBeaver AWS
-
CloudBeaver Enterprise
-
Deployment options
-
Development