-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 13.1k
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Rollup of 12 pull requests #77999
Rollup of 12 pull requests #77999
Conversation
This function was renamed.
For sub-items on a page don't show cfg that has already been rendered on a parent item. At its simplest this means not showing anything that is shown in the portability message at the top of the page, but also for things like fields of an enum variant if that variant itself is cfg-gated then don't repeat those cfg on each field of the variant. This does not touch trait implementation rendering, as that is more complex and there are existing issues around how it deals with doc-cfg that need to be fixed first.
…ack message when RUST_BACKTRACE=0
…ack message when RUST_BACKTRACE=0
The comment said it's UB to call lock() while it is locked. That'd be quite a useless Mutex. :) It was supposed to say 'locked by the same thread', not just 'locked'.
StaticMutex is only ever used with as a static (as the name already suggests). So it doesn't have to be generic over a lifetime, but can simply assume 'static. This 'static lifetime guarantees the object is never moved, so this is no longer a manually checked requirement for unsafe calls to lock().
This commit adjust `#[rustc_symbol_name]` so that it can be applied to non-monomorphic functions without producing an ICE. Signed-off-by: David Wood <[email protected]>
This commit modifies v0 symbol mangling to include all generic parameters from impl blocks (not just those used in the self type). Signed-off-by: David Wood <[email protected]>
…lnay Add std::thread::available_concurrency This PR adds a counterpart to [C++'s `std::thread::hardware_concurrency`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/hardware_concurrency) to Rust, tracking issue rust-lang#74479. cc/ @rust-lang/libs ## Motivation Being able to know how many hardware threads a platform supports is a core part of building multi-threaded code. In C++ 11 this has become available through the [`std::thread::hardware_concurrency`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/hardware_concurrency) API. Currently in Rust most of the ecosystem depends on the [`num_cpus` crate](https://docs.rs/num_cpus/1.13.0/num_cpus/) ([no.35 in top 500 crates](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1wwahRMHG3buvnfHjmPQFU4Kyfq15oTwbfsuZpwHUKc4/edit#gid=1253069234)) to provide this functionality. This PR proposes an API to provide access to the number of hardware threads available on a given platform. __edit (2020-07-24):__ The purpose of this PR is to provide a hint for how many threads to spawn to saturate the processor. There's value in introducing APIs for NUMA and Windows processor groups, but those are intentionally out of scope for this PR. See: rust-lang#74480 (comment). ## Naming Discussing the naming of the API on Zulip surfaced two options: - `std::thread::hardware_concurrency` - `std::thread::hardware_threads` Both options seemed acceptable, but overall people seem to gravitate the most towards `hardware_threads`. Additionally @jonas-schievink pointed out that the "hardware threads" terminology is well-established and is used in among other the [RISC-V specification](https://riscv.org/specifications/isa-spec-pdf/) (page 20): > A component is termed a core if it contains an independent instruction fetch unit. A RISC-V-compatible core might support multiple RISC-V-compatible __hardware threads__, or harts, through multithreading. It's also worth noting that [the original paper introducing C++'s `std::thread` submodule](http://www.open-std.org/jtc1/sc22/wg21/docs/papers/2007/n2320.html) unfortunately doesn't feature any discussion on the naming of `hardware_concurrency`, so we can't use that to help inform our decision here. ## Return type An important consideration @joshtriplett brought up is that we don't want to default to `1` for platforms where the number of available threads cannot be retrieved. Instead we want to inform the users of the fact that we don't know and allow them to handle that case. Which is why this PR uses `Option<NonZeroUsize>` as its return type, where `None` is returned on platforms where we don't know the number of hardware threads available. The reasoning for `NonZeroUsize` vs `usize` is that if the number of threads for a platform are known, they'll always be at least 1. As evidenced by the example the `NonZero*` family of APIs may currently not be the most ergonomic to use, but improving the ergonomics of them is something that I think we can address separately. ## Implementation @Mark-Simulacrum pointed out that most of the code we wanted to expose here was already available under `libtest`. So this PR mostly moves the internal code of libtest into a public API.
…ms, r=eddyb mangling: mangle impl params w/ v0 scheme This PR modifies v0 symbol mangling to include all generic parameters from impl blocks (not just those used in the self type) - an alternative fix to rust-lang#75326. ``` original: _RNCNvXCs4fqI2P2rA04_19impl_param_manglingINtB4_3FooppENtNtNtNtCsfnEnqCNU58Z_4core4iter6traits8iterator8Iterator4next0B4_ // |------------ B4_ ----------------| // _R (N C (N v (X (C ((s 4fqI2p2rA04_) 19impl_param_mangling)) (I (N t B4_ 3Foo) pp E) (N t (N t (N t (N t (C ((s fnEnqCNU58Z_) 4core)) 4iter) 6traits) 8iterator) 8Iterator)) 4next) 0) B4_ modified: _RNvXINICs4fqI2P2rA04_11issue_753260pppEINtB5_3FooppENtNtNtNtCsfnEnqCNU58Z_4core4iter6traits8iterator8Iterator4nextB5_ // _R (N v (X (I (N I (C ((s 4fqI2P2rA04_) 11issue_75326)) 0) ppp E) (I (N t B5_ 3Foo) pp E) (N t (N t (N t (N t (C ((s fnEnqCNU58Z_) 4core)) 4iter) 6traits) 8iterator) 8Iterator)) 4next) B5_ // | ^ | // | | | // | new impl namespace | ``` ~~Submitted as a draft as after some discussion w/ @eddyb, I'm going to do some investigation into (yet more alternative) changes to polymorphization that might remove the necessity for this.~~ r? @eddyb
…n, r=nikomatsakis Stabilize move_ref_pattern # Implementation - Initially the rule was added in the run-up to 1.0. The AST-based borrow checker was having difficulty correctly enforcing match expressions that combined ref and move bindings, and so it was decided to simplify forbid the combination out right. - The move to MIR-based borrow checking made it possible to enforce the rules in a finer-grained level, but we kept the rule in place in an effort to be conservative in our changes. - In rust-lang#68376, @Centril lifted the restriction but required a feature-gate. - This PR removes the feature-gate. Tracking issue: rust-lang#68354. # Description This PR is to stabilize the feature `move_ref_pattern`, which allows patterns containing both `by-ref` and `by-move` bindings at the same time. For example: `Foo(ref x, y)`, where `x` is `by-ref`, and `y` is `by-move`. The rules of moving a variable also apply here when moving *part* of a variable, such as it can't be referenced or moved before. If this pattern is used, it would result in *partial move*, which means that part of the variable is moved. The variable that was partially moved from cannot be used as a whole in this case, only the parts that are still not moved can be used. ## Documentation - The reference (rust-lang/reference#881) - Rust by example (rust-lang/rust-by-example#1377) ## Tests There are many tests, but I think one of the comperhensive ones: - [borrowck-move-ref-pattern-pass.rs](https://github.com/Centril/rust/blob/85fbf49ce0e2274d0acf798f6e703747674feec3/src/test/ui/pattern/move-ref-patterns/borrowck-move-ref-pattern-pass.rs) - [borrowck-move-ref-pattern.rs](https://github.com/Centril/rust/blob/85fbf49ce0e2274d0acf798f6e703747674feec3/src/test/ui/pattern/move-ref-patterns/borrowck-move-ref-pattern.rs) # Examples ```rust #[derive(PartialEq, Eq)] struct Finished {} #[derive(PartialEq, Eq)] struct Processing { status: ProcessStatus, } #[derive(PartialEq, Eq)] enum ProcessStatus { One, Two, Three, } #[derive(PartialEq, Eq)] enum Status { Finished(Finished), Processing(Processing), } fn check_result(_url: &str) -> Status { // fetch status from some server Status::Processing(Processing { status: ProcessStatus::One, }) } fn wait_for_result(url: &str) -> Finished { let mut previous_status = None; loop { match check_result(url) { Status::Finished(f) => return f, Status::Processing(p) => { match (&mut previous_status, p.status) { (None, status) => previous_status = Some(status), // first status (Some(previous), status) if *previous == status => {} // no change, ignore (Some(previous), status) => { // Now it can be used // new status *previous = status; } } } } } } ``` Before, we would have used: ```rust match (&previous_status, p.status) { (Some(previous), status) if *previous == status => {} // no change, ignore (_, status) => { // new status previous_status = Some(status); } } ``` Demonstrating *partial move* ```rust fn main() { #[derive(Debug)] struct Person { name: String, age: u8, } let person = Person { name: String::from("Alice"), age: 20, }; // `name` is moved out of person, but `age` is referenced let Person { name, ref age } = person; println!("The person's age is {}", age); println!("The person's name is {}", name); // Error! borrow of partially moved value: `person` partial move occurs //println!("The person struct is {:?}", person); // `person` cannot be used but `person.age` can be used as it is not moved println!("The person's age from person struct is {}", person.age); } ```
…_the_top_of_the_query_stack, r=oli-obk ICEs should always print the top of the query stack see rust-lang#76920
…ulacrum BTreeMap: test invariants more thoroughly and more readably r? @Mark-Simulacrum
…r, r=dtolnay Use futex-based thread-parker for Wasm32. This uses the existing `sys_common/thread_parker/futex.rs` futex-based thread parker (that was already used for Linux) for wasm32 as well (if the wasm32 atomics target feature is enabled, which is not the case by default). Wasm32 provides the basic futex operations as instructions: https://webassembly.github.io/threads/syntax/instructions.html These are now exposed from `sys::futex::{futex_wait, futex_wake}`, just like on Linux. So, `thread_parker/futex.rs` stays completely unmodified.
…-mutex, r=dtolnay For backtrace, use StaticMutex instead of a raw sys Mutex. The code used the very unsafe `sys::mutex::Mutex` directly, and built its own unlock-on-drop wrapper around it. The StaticMutex wrapper already provides that and is easier to use safely. @rustbot modify labels: +T-libs +C-cleanup
…ex, r=dtolnay Static mutex is static StaticMutex is only ever used with as a static (as the name already suggests). So it doesn't have to be generic over a lifetime, but can simply assume 'static. This 'static lifetime guarantees the object is never moved, so this is no longer a manually checked requirement for unsafe calls to lock(). @rustbot modify labels: +T-libs +A-concurrency +C-cleanup
…oudabi-sync, r=dtolnay Cleanup cloudabi mutexes and condvars This gets rid of lots of unnecessary unsafety. All the AtomicU32s were wrapped in UnsafeCell or UnsafeCell<MaybeUninit>, and raw pointers were used to get to the AtomicU32 inside. This change cleans that up by using AtomicU32 directly. Also replaces a UnsafeCell<u32> by a safer Cell<u32>. @rustbot modify labels: +C-cleanup
Simplify doc-cfg rendering based on the current context For sub-items on a page don't show cfg that has already been rendered on a parent item. At its simplest this means not showing anything that is shown in the portability message at the top of the page, but also for things like fields of an enum variant if that variant itself is cfg-gated then don't repeat those cfg on each field of the variant. This does not touch trait implementation rendering, as that is more complex and there are existing issues around how it deals with doc-cfg that need to be fixed first. ### Screenshots, left is current, right is new: 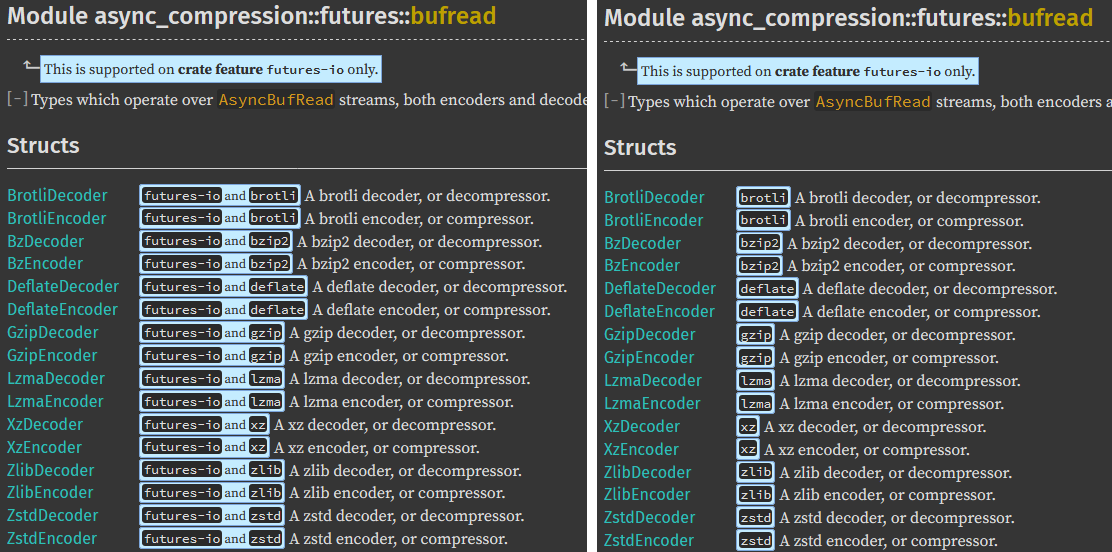    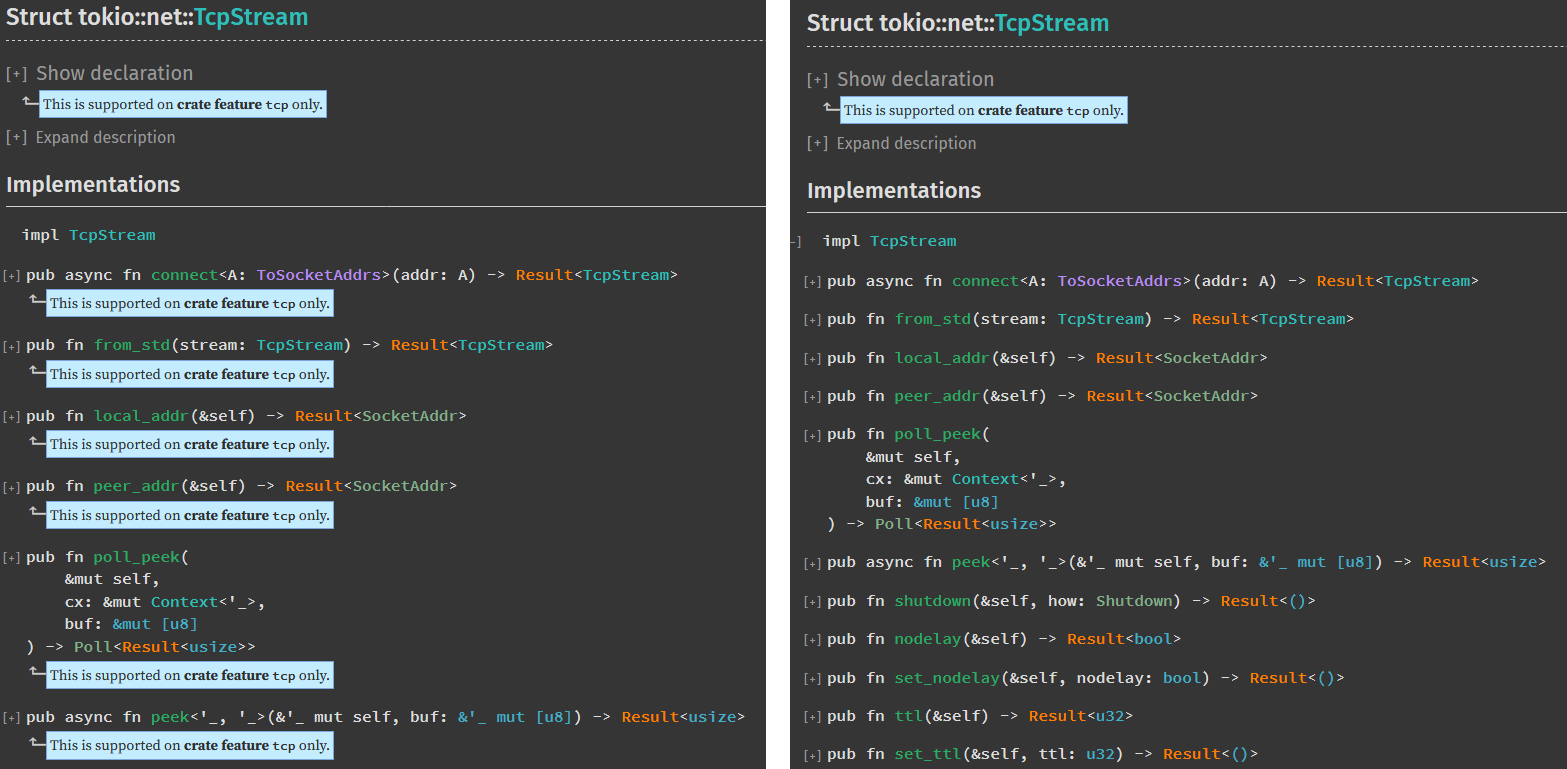 cc rust-lang#43781
…, r=oli-obk
rustc_parse: fix spans on cast and range exprs with attrs
Currently the span for cast and range expressions does not include the span of attributes associated to the lhs which is causing some issues for us in rustfmt.
```rust
fn foo() -> i64 {
#[attr]
1u64 as i64
}
fn bar() -> Range<i32> {
#[attr]
1..2
}
```
This corrects the span for cast and range expressions to fully include the span of child nodes
Fix intra doc link for needs_drop It currently links to itself. Oops. r? @jyn514
|
📌 Commit ff490d3 has been approved by |
|
⌛ Testing commit ff490d3 with merge fb0296f45bd42862f3d7c0bf2ff22fc637703250... |
|
Your PR failed (pretty log, raw log). Through arcane magic we have determined that the following fragments from the build log may contain information about the problem. Click to expand the log.I'm a bot! I can only do what humans tell me to, so if this was not helpful or you have suggestions for improvements, please ping or otherwise contact |
|
💔 Test failed - checks-actions |
Successful merges:
std::thread::available_concurrency#74480 (Add std::thread::available_concurrency)Failed merges:
r? @ghost