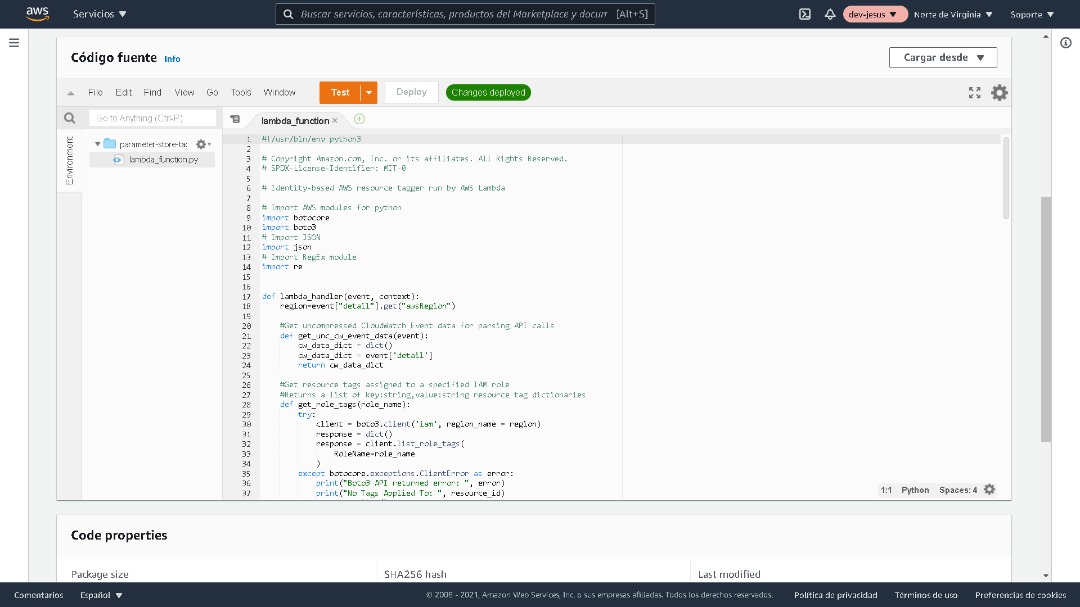
The auto-tagging solution described in this post applies your organization’s required tags to newly created resources using an automated workflow. It includes a rule created in Amazon CloudWatch Events, a resource tag repository such as AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store, and an AWS Lambda function.
By following the steps in this post, you create a CloudWatch event rule, Parameter Store entries, and a Lambda function to enable the auto-tagging solution explained in this post.
- A user creates Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances.
- A user creates Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances.
- A CloudWatch event rule monitors and is triggered upon the creation of events like RunInstances.
- The CloudWatch event rule detects an applicable event, and then invokes a Lambda function to tag the resources.
- Lambda retrieves the required tags from Parameter Store and tags the new resource.
You’ll find the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions policy document, IAM trust policy document, and Lambda function in this GitHub repo. Run the git clone command to clone this GitHub repo to your local machine:
You need a CloudTrail trail to detect and respond to AWS resource creation API events. If you do not already have a trail, follow the steps in Creating a Trail in the AWS CloudTrail User Guide. Here is an example AWS CLI command for creating a trail for this auto-tagging solution:
aws cloudtrail create-trail --name resource-creation-events --s3-bucket-name blog-demos
The Amazon EC2 RunInstances API CloudTrail event provides a lot of tagging information. For example, you can extract:
- The single sign-on (SSO) user ID of the entity that created the resource from the
principalIdkey - The
IAM rolethe entity assumed during resource creation from the arn key. - The
date/timeof resource creation from theeventTimekey. - The EC2 instance ID from
instanceId.
This CloudTrail event also provides detail about other resources that were created or updated when the EC2 instance was created. This means you can extract and automatically tag your instances with detail like the VPC ID and subnet ID.
There are two options for storing your required resource tag keys and values. You can use either or both of these options.
Option 1: Apply your required resource tags to the resource creator’s IAM role. When the resource creator assumes the role to create a resource, the Lambda function described in this blog post retrieves the resource tags assigned to that IAM role. The Lambda function then applies those retrieved IAM role tags to the newly created AWS resource.
Option 2: Use AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store to store tags per resource creator role or SSO user ID using a hierarchy called a path. For this example, use this path partitioning scheme:
/auto-tag/IAM_Role/User_ID/tag/tag_key/tag_value
Here is an example AWS CLI command to create a tag entry in Parameter Store. This example path sets this tag’s key to team and its value to SouthEast-migration.
aws ssm put-parameter --name /auto-tag/sso-role1/sso-user1/tag/team --value SouthEast-migration --type SecureString
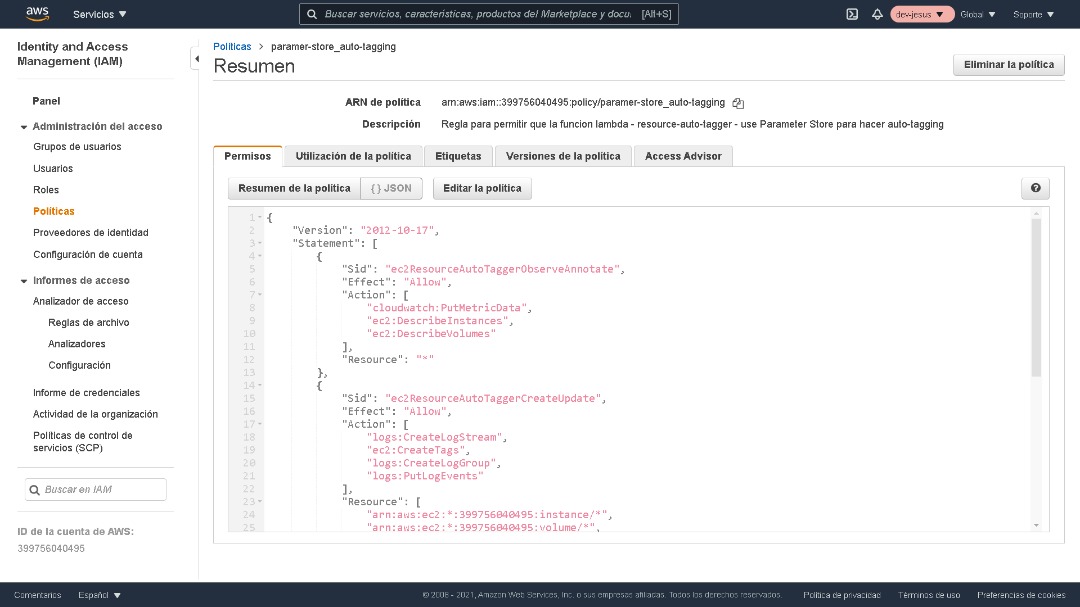
The resource-auto-tagger Lambda function used in this solution needs permission to interact with other AWS services on your behalf. Create an IAM permissions policy that allows the Lambda function to invoke the service actions shown in the following table.
Create an IAM permissions policy for the AWS services and actions shown in the table, and then assign that policy to an IAM role the resource-auto-tagger Lambda function assumes every time it is run. The GitHub repo you cloned in step 1 of this post contains an example IAM permissions policy and an example IAM trust policy.
The following example AWS CLI commands create an IAM permissions policy and link it to the IAM role. (Replace 123456789012 in the example command with your AWS account number.)
aws iam create-policy --policy-name resource-auto-tagger-lambda-permissions-policy --policy-document file://iam-lambda-role-permissions-policy.json
aws iam create-role --role-name resource-auto-tagger-lambda-role --assume-role-policy-document file://iam-lambda-role-trust-policy.json
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name resource-auto-tagger-lambda-role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:policy/resource-auto-tagger-lambda-permissions-policy
Now, use the AWS CLI to create the Lambda function that performs the resource tagging when it is triggered by the CloudWatch event rule. This Lambda function uses the Python 3.8 runtime.
The following example AWS CLI command creates the resource-auto-tagger Lambda function. (Replace 123456789012 in the example command with your AWS account number.)
aws lambda create-function --function-name resource-auto-tagger --runtime python3.8 --role arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/resource-auto-tagger-lambda-role --timeout 6 --code S3Bucket=blog-demos,S3Key=auto-tag/resource-auto-tagger.zip,S3ObjectVersion=null --handler lambda_handler
Create a rule in CloudWatch Events to trigger on the Amazon EC2 RunInstances API action. For information, see Creating a CloudWatch Events Rule That Triggers on an AWS API Call Using AWS CloudTrail in the Amazon CloudWatch Events User Guide. Use the following settings for the rule:
- For Event source, choose Event Pattern.
- For Service Name, choose EC2.
- For Event Type, choose AWS API Call via CloudTrail.
- Choose Specific operation(s), and then enter RunInstances.
- For Targets, choose the Lambda function you created in Step 5.
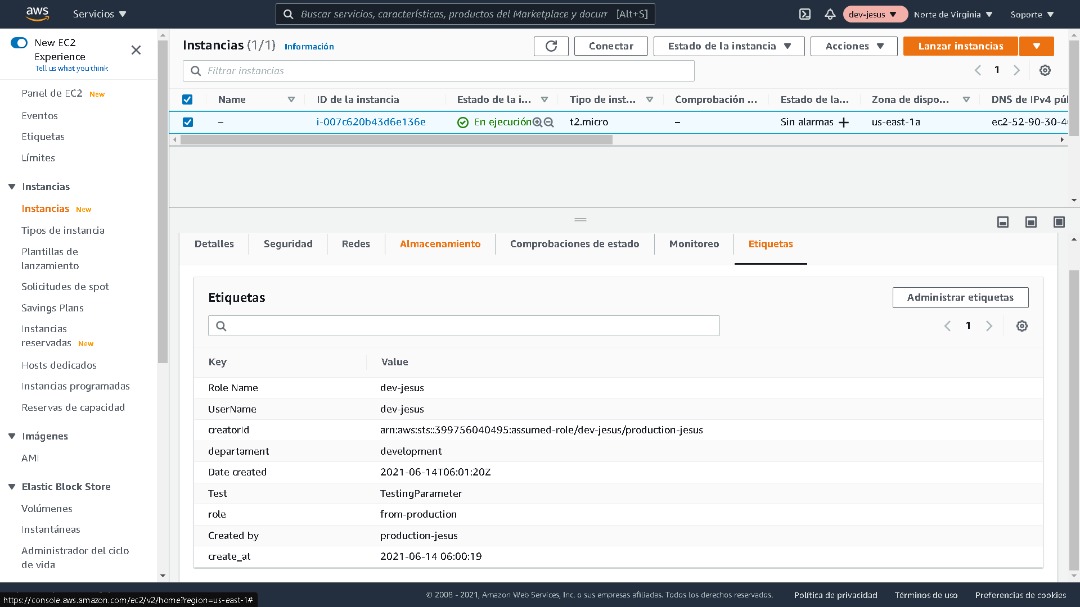
After you deploy your Lambda function and give it the appropriate IAM permissions through an assigned IAM role, create your Parameter Store repository. This repository will store your required resources tags by identity and role. Now you can test and verify the auto-tagging functionality by simply creating an EC2 instance in your AWS account.
The following example AWS CLI command creates an EC2 instance:
aws ec2 run-instances --image-id ami-0c94855ba95c71c99 --instance-type t2.micro --key-name your_key --tag-specifications 'ResourceType=instance,Tags=[{Key=Name,Value=auto-tag-example-1}]'
CloudTrail delivers API events within 15 minutes of their occurrence. After you create the instance, wait 15 minutes, and then check the tags assigned to the instance to verify the resource-auto-tagger Lambda function automatically applied the required tags.
The following AWS CLI command shows how to view the resource tags applied to the new EC2 instance:
aws ec2 describe-tags --filters
To avoid charges after you test the auto-tagging function, delete the Lambda function. The following example AWS CLI command deletes the Lambda function:
aws lambda delete-function --function-name resource-auto-tagger
If you entered resource tags into Systems Manager Parameter Store, here is an example AWS CLI command to delete them:
aws ssm delete-parameter --name /auto-tag/sso-role1/sso-user1/tag/team
In this post, I showed how when CloudTrail reports a watched API call, a CloudWatch event rule will trigger a Lambda function that automatically tags newly created EC2 instances with your required tags. The Parameter Store in AWS Systems Manager provides a hierarchical and secure way to store your required resource tags organized by user identity and IAM role. Using this auto-tagging technique with other service creation API calls, such as the CreateBucket action in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), you can create additional CloudWatch event rules and Lambda functions to automatically tag other AWS resource types as your builders and automation tools create them.