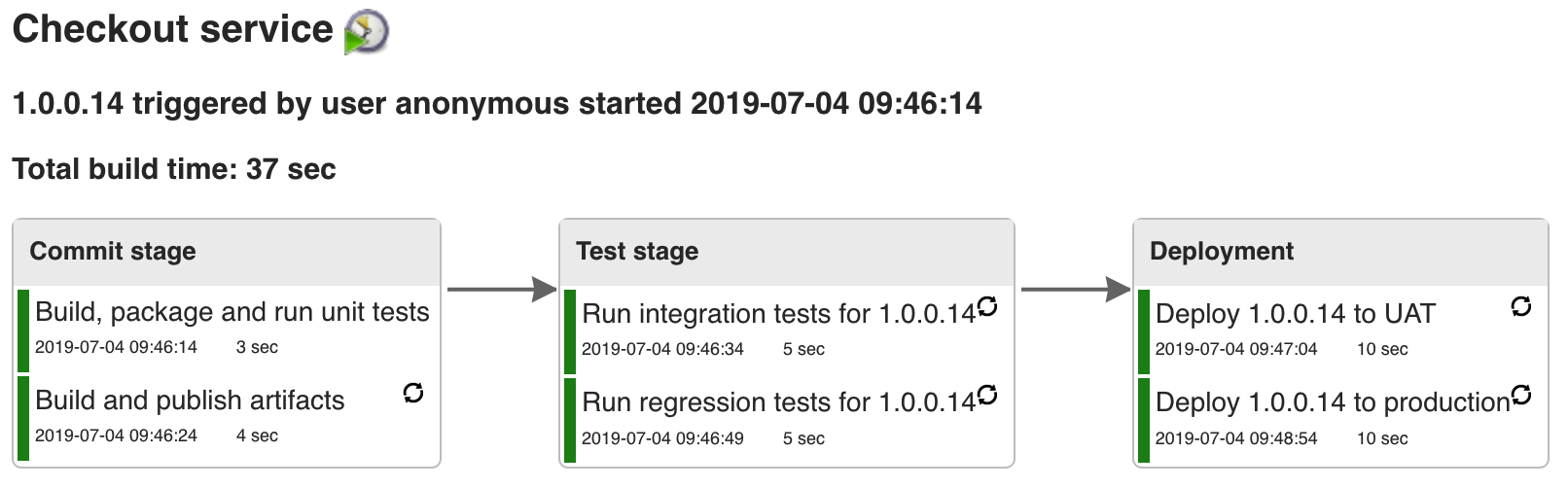
The purpose of the Delivery Pipeline plugin is to provide visualisation of delivery/build pipelines in Jenkins. The plugin is perfect for Continuous Delivery pipeline visualisation on information radiators.
In Continuous Delivery, fast feedback and visualisation of the delivery process is one of the most important aspects. When using Jenkins as a build server it is now possible to visualise one or more delivery pipelines in the same view (even in full screen!) using the Delivery Pipeline plugin. You can install the Delivery Pipeline plugin using the Jenkins plugin management.
Project wiki page can be found here: Delivery Pipeline Plugin - Wiki.
We use the official Jenkins issue tracker for bugs, improvements and new features. Please report any issues on component delivery-pipeline-plugin.
This plugin has been contributed to the community by Diabol AB.
Delivery Pipeline plugin 1.4.0 and later requires Java 8 and Jenkins core 2.164 or later (Java 11 required for plugin development).
Delivery Pipeline plugin 1.3.0 and later requires Java 8 and Jenkins core 2.73.3 or later.
Delivery Pipeline plugin 1.2.0 and later requires Java 8 and Jenkins core 2.62 or later.
Delivery Pipeline plugin 1.1.0 and later requires Java 8 and Jenkins core 1.642.3 or later.
Delivery Pipeline plugin 1.0.0 and later requires Java 7 and Jenkins core 1.642.3 or later.
Delivery Pipeline plugin 0.10.3 requires Java 6 and Jenkins core 1.565 or later.
Requires Java 11, Apache Maven 3.3.x or later.
mvn clean install
The project contains a rigorous test suite which takes some time to run. If you just want to build the project for the first time, you can shortcut it by running:
mvn clean install -DskipTests
During development you can easily start a local Jenkins instance with the Delivery Pipeline plugin installed based on your current source code revision. Build the project using the step mentioned above and run:
mvn hpi:run
This will start a local Jenkins with the Delivery Pipeline plugin installed. It will by default be available at http://localhost:8080/jenkins.
To bootstrap your local Jenkins instance with jobs, you can use the provided examples.
You would need to have Jenkins Job Builder (JJB) or JobDSL available in order to use them. To use the JJB .yaml job configurations without the need to install JJB explicitly, you could run it in a Docker container. Provide the example jenkins.ini to JJB. When running inside a container, you might need to add your host ip address in the jenkins.ini instead of localhost to allow JJB to connect to your Jenkins instance. Mount the examples directory to the Docker container, and then invoke JJB ising the jenkins-jobs command, such as:
docker run -it --rm --net=host -v PATH_TO/delivery-pipeline-plugin/examples/jenkins.ini:/etc/jenkins_jobs/jenkins_jobs.ini -v PATH_TO/delivery-pipeline-plugin/examples:/root/jenkins-job-builder tynja/jenkins-job-builder jenkins-jobs update demo.yaml
The project contains a set of functional tests that run in a separate Maven goal. These can be run using:
mvn integration-test
To create a Jenkins plugin artifact, build the project and run:
mvn hpi:hpi
This creates a delivery-pipeline-plugin.hpi file in the target directory. This file can be manually uploaded through the Jenkins plugin management console (under the Advanced tab) to load the built plugin into Jenkins.
To build and run the Delivery Pipeline plugin together with Jenkins in a Docker container, you first need to build the project before building the Docker image:
mvn clean package
docker build -t dpp .
docker run -p 8080:8080 dpp
You can then access your local Jenkins instance on http://localhost:8080.
If you just want to run Jenkins and the Delivery Pipeline plugin in a Docker container without building it yourself, you can pull certain versions from Docker hub:
docker pull diabol/delivery-pipeline-plugin:1.3.0
docker run -it -p 8080:8080 diabol/delivery-pipeline-plugin:1.3.0
The Docker container will be bootstrapped with a few Jenkins job configurations and a delivery pipeline view. Jenkins will be available at http://localhost:8080.
Configuring manually triggered jobs for views based on traditional Jenkins jobs with downstream dependencies
Note: This requires the Build Pipeline plugin to be installed.
To be able to configure a certain job in the pipeline as a manual step, you have to configure the upstream job that triggers the job which is to be performed manually to be marked as a manual step.
In the Jenkins UI this shows up as a Post-Build Action: Build other projects (manual step), where you configure the name of the job to be manually triggered in the "Downstream Project Names".
If you're creating your jobs with JobDSL, use the following syntax in the publishers section (parameters is optional):
publishers {
buildPipelineTrigger('name-of-the-manually-triggered-job') {
parameters {
propertiesFile('env.${BUILD_NUMBER}.properties')
}
}
}
In your pipeline configuration, make sure to enable manual triggers. The manual triggers (a play button) will not be shown in the UI for aggregate pipelines, only for pipeline instances. If you want to access manual triggers from the UI, make sure to show at least one pipeline instance.
Here is an example of a corresponding JobDSL pipeline view configuration:
deliveryPipelineView("my-pipeline") {
name("my-pipeline")
description("Delivery pipeline with a manual trigger")
pipelineInstances(1)
showAggregatedPipeline(false)
columns(1)
updateInterval(2)
enableManualTriggers(true)
showAvatars(false)
showChangeLog(true)
pipelines {
component("My pipeline", "the-name-of-the-first-job-in-the-pipeline")
}
}
Here is an example of how to specify a custom CSS for the Delivery Pipeline Plugin using a JobDSL pipeline view configuration:
deliveryPipelineView("my-pipeline") {
name("my-pipeline")
description("Delivery pipeline with custom full screen CSS")
pipelineInstances(1)
showAggregatedPipeline(false)
columns(1)
updateInterval(2)
enableManualTriggers(true)
showAvatars(false)
showChangeLog(true)
configure { node ->
node << {
fullScreenCss('https://my-jenkins-instance/userContent/my-pipeline-fullscreen.css')
}
}
pipelines {
component("My pipeline", "the-name-of-the-first-job-in-the-pipeline")
}
}
Example configurations can be found in the examples subdirectory.
For Jenkins Job Builder job configuration examples, see: demo.yaml
For JobDSL job configuration examples, see: demo.groovy
For examples on how to use the Jenkins pipeline task step to visualize steps within a stage, see this example pipeline
Read GitHub's general contribution guidelines: https://guides.github.com/activities/contributing-to-open-source/#contributing
It basically comes down to the following guidelines:
- If applicable, create a Jira issue
- Make sure a similar issue doesn't already exist
- Fork the repo
- Contribute and have fun!
- Add as much unit testing as possible to any new code changes
- This will make the code much more easy to maintain and to understand its intent
- Make sure your code is well formatted and aligns with the projects code style conventions. This will be enforced by the CI build that runs on each pull request.
- Make sure to prefix the commit message with the associated Jira issue number together with a descriptive commit message
- Create a pull request to start a discussion and to get feedback from the maintainers
- Add a link to the pull request in the associated Jira issue
If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to one of the maintainers: