This package is the core used by the Urpflanze javascript library to generate the scene.
It deals with creating two-dimensional shapes, repeating them, manipulating them point by point and encapsulating them.
You can use it in the browser or in node.
The creation of this library comes from the need to create simple APIs for manage the repetition of primitive shapes and the possibility of applying transformations to each of them, applying transformations on the points avoiding the use of canvas transformations.
Another need - which then became one of the main features - was to be able to encapsulate the result of a generation and manage it as if it were a new shape.
I am trying to create a tool for those who want to approach the world of programming or for programmers who want to approach the world of creative coding.
I have spent a lot of time and will spend more to support this project. I also have in mind a web editor (open-source) where you can use the features of this library in the browser.
You can see a preview here
- Synopsis
- Motivations
- Donate
- Menu
- Installation
- Creating a shape
- Primitive shapes - ShapeBuffer - ShapeLoop
- Repetitions
- Manage repetitions
- Encapsulation
- Recursion
- ShapeFollow
- Vertex Callback
- Scene
- Examples
You can install the library with the command:
npm i @urpflanze/core --saveAt the end you can import Urpflanze into your project
/**
* Full importing
*/
import * as Urpflanze from '@urpflanze/core'
const scene = new Urpflanze.Scene()
/**
* Selective import
*/
import { Scene } from '@urpflanze/core'
const scene = new Scene()The ShapeBuffer is the shape to which you can pass a buffer of points.
It accepts the shape property which is an array of points [x0, y0, x1, y1, ..., xn, yn].
The array of points will be adapted between a range of -1 and 1.
Example:
import { ShapeBuffer } from '@urpflanze/core'
const rect = new ShapeBuffer({
shape: [-1, -1, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1],
sideLength: [10, 10],
})
rect.generate() // Apply properties
console.log(rect.getBuffer())
// Output:
// Float32Array(8) [
// -10, -10, 10, -10,
// 10, 10, -10, -10
// ]The ShapeLoop is a shape generated by a loop, it is recommended to return values between a range of -1 and 1
import { ShapeLoop } from '@urpflanze/core'
const circle = new Urpflanze.ShapeLoop({
sideLength: [10, 10],
loop: {
start: 0,
end: Math.PI * 2,
inc: (Math.PI * 2) / 100, // (end - start) / 100 for generate 100 points
vertex: shapeLoopRepetition => [
// shapeLoopRepetition.current start from 0 and end to 2 PI,
// so you can use it as a angle
Math.cos(shapeLoopRepetition.current),
Math.sin(shapeLoopRepetition.current),
],
},
bClosed: true, // flag to determinate the shape is closed
})
circle.generate()
console.log(circle.getBuffer().length)
// Output:
// 200 / 2 = 100 pointsIn this package there are already some primitive shapes.
You can use the static getBuffer method to receive a buffer.
console.log(Urpflanze.Rect.getBuffer(/*{ ...props }*/))
// Float32Array(8) [
// 1, 1, -1, 1,
// -1, -1, 1, -1
// ]List of all primitives:
Polygon
Circle
Lissajous
Spiral
Rose
SuperShape
On primitive shapes you can apply modifiers to the buffer before transformations are applied:
const squircle = new Urpflanze.Rect({
modifiers: [new Urpflanze.Modifiers.Smooth({ level: 3, tension: 0.3 })],
})The list of modifiers is:
Adapt: Fit the shape into a rectangleClose: Adds a close point to the bufferMirror: clones the shape on the x, y axesOffset: Slice of a bufferSmooth: Makes the shape smootherSubdivide: Adds midpoints on the edges of the shapeSolidify: (in progress) Tread the edge of the shape
Using Urpflanze you can manage two types of repetitions: ring or matrix.
For this type of repetition you can set a numeric value to the repetitions property to indicate the number of times it will repeat and the distance property to indicate the distance from the center.
const rects = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: 8,
distance: 100,
sideLength: 25,
})Basically the shapes will be rotated towards the center, if you want to avoid this effect you have to rotate the vorma inversely to the current angle of the repetition.
const rects = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: 8,
sideLength: 25,
distance: 100,
rotateZ: ({ repetition }) => -repetition.angle,
})To repeat the shape as an array, just pass an Array of numbers indicating the number of rows and columns to the repetitions property. The distance property in this case will also be an Array containing the distance between the rows and columns.
const matrix = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: [3, 4],
sideLength: 20,
distance: [80, 50],
})To manage the repetitions you can pass a function to the properties instead of a constant.
The argument of the function which is of type IPropArguments.
Inside it we find the repetition property which - like any object that implements a IBaseRepetition - contains the following properties:
indexthe current index, from 1 to countcountthe total number of repetitionsoffsetan index ranging from 0 to 1 which does not depend on the number of repetitions. For example, if the number of repetitions is 3, the offset value will be 0 - 0.5 - 1
For matrix repetitions you can also use repetition.row and repetition.col also of type IBaseRepetition
const spiral = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: 8,
sideLength: 25,
distance: ({ repetition }) => repetition.offset * 100,
scale: ({ repetition }) => repetition.offset,
})const matrix = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: [4],
sideLength: 25,
distance: 50,
scale: ({ repetition }) => {
// [0, 0] is center of repetition, you can set value between [-1, -1] (left - top angle) and [1, 1] (right - bottom angle)
return Urpflanze.distanceFromRepetition(repetition, [0, 0]),
}
})To be able to encapsulate a shape you can use the Shape class to which you can pass the property
shape which is a ShapePrimitive (ShapeBuffer or ShapeLoop) or a Group.
const lines = new Urpflanze.Line({
repetitions: 20,
sideLength: 25,
distance: 50,
})
const container = new Urpflanze.Shape({
shape: lines,
repetitions: [3], // [3, 3]
distance: 100,
scale: 0.5, // scale all repetitions of lines
})
const final = new Urpflanze.Shape({
shape: container,
repetitions: 6,
distance: 120,
scale: 0.4,
perspective: 0.99,
rotateY: Urpflanze.toRadians(60),
})| lines | container | final |
|---|---|---|
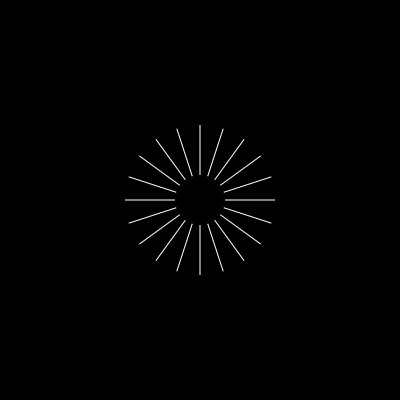 |
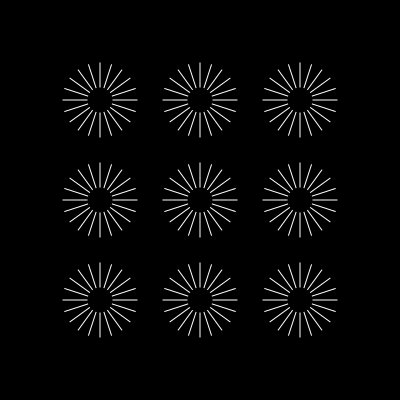 |
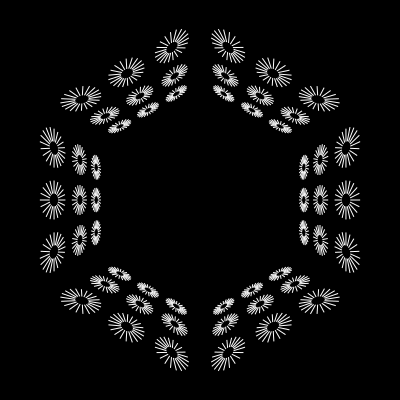 |
const group = new Urpflanze.Group({
repetitions: 4,
sideLength: 15,
distance: 25,
rotateZ: Urpflanze.toRadians(45),
})
group.add(
new Urpflanze.Circle(),
new Urpflanze.Rect(),
new Urpflanze.Line({
rotateZ: 0,
})
)
const shape = new Urpflanze.Shape({
shape: group,
repetitions: 8,
distance: 100,
rotateZ: ({ repetition }) => -repetition.angle,
})| group | shape |
|---|---|
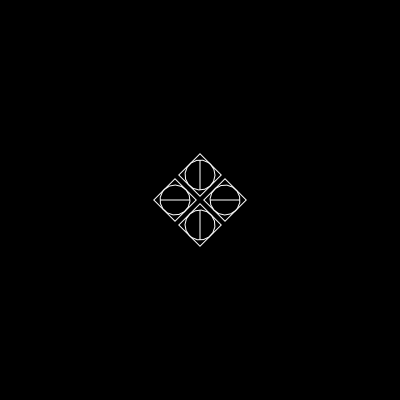 |
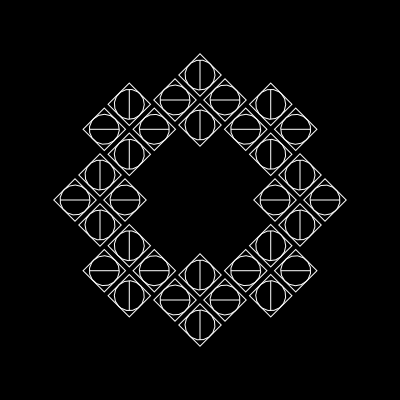 |
You can use the repetition object of whoever encapsulates a shape by setting the shapeUseParent property.
This parameter is optional since a new buffer of points will be generated at each repetition of the encapsulator.
const rects = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: [5],
sideLength: 10,
distance: 20,
scale: ({ repetition, parent }) => {
return repetition.offset * parent.repetition.offset
},
})
const container = new Urpflanze.Shape({
shapeUseParent: true, // <--
shape: rects,
repetitions: [5],
distance: 50,
scale: 0.4,
})Another possibility is to use the ShapeRecursive to repeat any Shape on each of its points.
You can use the recursion property of type IRecursionRepetition
const rect = new Urpflanze.Rect({
sideLength: 50,
})
const container = new Urpflanze.ShapeRecursive({
// shapeUseRecursion: true,
// [prop]: ({ recursion }) => ...
shape: rect,
recursionScale: 2,
recursions: 4,
})With the ShapeFollow you can repeat the shape on each point of the follow
In this example we can also see the use of the interpolation function between buffers:
/**
* Repeat a Polygon on the buffer that morphs from Rect to Star
*
* for animation using https://github.com/urpflanze-org/animation
* and https://github.com/urpflanze-org/drawer-canvas for draw and rendering
*/
const scene = new Urpflanze.Scene()
const [from, to] = Urpflanze.prepareBufferForInterpolation(
Urpflanze.Rect.getBuffer({
modifiers: [new Urpflanze.Modifiers.Smooth({ closed: false, tension: 0.3, level: 4 })],
}),
Urpflanze.Star.getBuffer({
spikes: 6,
innerRadius: 1.3,
modifiers: [new Urpflanze.Modifiers.Smooth({ closed: false, tension: 0.7, level: 5 })],
})
)
scene.add(
new Urpflanze.ShapeFollow({
shape: new Urpflanze.Polygon({
sideNumber: 6,
sideLength: 20,
rotateZ: t => {
const d = 2000
const o = Math.cos(t.parent.follow.offset * Urpflanze.PI2) * 500 // set shapeUseFollor for bind follow IBaseRepetition
const time = Animation.clock(scene.currentTime, d - o, true, 'normal', o)
return Animation.Easings.quadraticOut(time, 0, Urpflanze.PI2, d - o)
},
drawer: {
stroke: '#ffffff22',
},
}),
follow: new Urpflanze.ShapeBuffer({
sideLength: 100,
shape: () => {
// Interpolate Rect (from) and Star (to) with easing
return Urpflanze.interpolate(
from,
to,
Animation.Easings.elasticInOut(Animation.clockOffset(scene.currentTime, 2000), 0, 1, 1, 1.2)
)
},
}),
shapeUseFollow: true, // use follow repetition in Rect (for rotateZ)
})
)
const drawer = new DrawerCanvas(scene, document.body, {}, 4000, 24)
drawer.startAnimation()The vertexCallback property is a function that is called at each point of the shape of each repetition.
The function takes 3 arguments:
vertex: [number, number] current vertexvertexRepetition: IBaseRepetition for the vertices of the current repetitionpropArguments: IPropArguments
const rects = new Urpflanze.Rect({
repetitions: [10, 1],
sideLength: 100,
scale: propArguments => propArguments.repetition.row.offset * 0.95 + 0.05,
modifiers: new Urpflanze.Modifiers.Subdivide({ level: 5 }),
vertexCallback: (vertex, vertexRepetition, propArguments) => {
const angle = Math.atan2(vertex[1], vertex[0])
const x = Math.cos(angle)
const y = Math.sin(angle)
const offset = propArguments.repetition.row.offset ** 2 * 20
const noise = Urpflanze.noise('seed', vertexRepetition.offset * 10) * offset
vertex[0] += x * noise
vertex[1] += y * noise
},
})You can use the shapes independently or you can add them to a scene. When a shape is added to the scene it will be arranged in the center of it, adding an offset to all points.
Use without the scene:
const rect = new Urpflanze.Rect({ sideLength: 25 })
rect.generate()
console.log(rect.getBounding())
// Output:
//
// { cx: 0, cy: 0, x: -25, y: -25, width: 50, height: 50 }
// # left, top point: (-25, -25) | right, bottom point: (25, 25)Using the scene:
const scene = new Urpflanze.Scene({ width: 100, height: 100 })
const rect = new Urpflanze.Rect({ sideLength: 25 })
scene.add(rect)
scene.update()
console.log(rect.getBounding())
// Output:
//
// {
// cx: 50, cy: 50, # Center of scene
// x: 25, y: 25, # Center of scene - sideLength
// width: 50, height: 50 # sideLength * 2
// }
// # left, top point: (25, 25) | right, bottom point: (75, 75)When you call the generate() method on a shape a buffer of type Array<IBufferIndex> is created containing the information on the current repetition of shape and the reference index of the total buffer (getBuffer())
if repetitions are statica (and ShapeLoop has static loop) the IndexedBuffer will only generate once.
// scene.add(...)
const time = Date.now()
scene.currentTime = time
const sceneChilds = scene.getChildren()
for(let i = 0, len = sceneChilds.length; i < len; i++) {
// Generate Buffer and IndexedBuffer
sceneChilds[i].generate(time, true)
// Buffer of indexing (https://docs.urpflanze.org/core/#/ref/IBufferIndex)
const childIndexedBuffer = sceneChilds[i].getIndexedBuffer()
const childBuffer = sceneChilds[i].getBuffer()
let childVertexIndex = 0
for (let currentBufferIndex = 0, currentBufferIndex < childIndexedBuffer.length; currentBufferIndex++) {
const currentIndexing = childIndexedBuffer[currentBufferIndex]
beginPath()
moveTo(childBuffer[childVertexIndex], childBuffer[childVertexIndex + 1])
childVertexIndex += 2
for (let currentFrameLength = childVertexIndex + currentIndexing.frameLength - 2; childVertexIndex < currentFrameLength; childVertexIndex += 2)
lineTo(childBuffer[childVertexIndex], childBuffer[childVertexIndex + 1])
if (currentIndexing.shape.isClosed())
closePath()
fillOrStrokePath()
}
}Draw point in a console (using this package)
 |
 |
Pen plotter