CLI Tool & importable library for evaluating object detection performance with mAP (mean Average Precision) scores.
The higher your mAP score the better your model is performing.
#Citation & Contributions
This repository is a fork of Cartucho/mAP 
-
João Cartucho - Imperial College London
- credit for original scripts & paper submission, explanation, etc.
-
- while at Mission Systems Pty. Ltd. conversion to CLI flexible tool and importable library to allow this codebase to be used programatically within other Python programs.
Install PyQt5 the right way - the pip3 installation can be a little unstable.
sudo apt-get install python3-pyqt5
sudo apt-get install pyqt5-dev-tools
sudo apt-get install qttools5-dev-tools
pip3 install requirements.txt
python3 evaluate_mAP_scores.py [-h] -pd PREDICTION_DIR -gt GROUND_TRUTH_DIR [-id IMAGE_DIR]
[-od OUTPUT_DIR] [-a] [-np] [-q] [-i IGNORE [IGNORE ...]]
[--set-class-iou SET_CLASS_IOU [SET_CLASS_IOU ...]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-pd PREDICTION_DIR, --prediction_dir PREDICTION_DIR
path to predicted annotations
-gt GROUND_TRUTH_DIR, --ground_truth_dir GROUND_TRUTH_DIR
path to ground truth annotations
-id IMAGE_DIR, --image_dir IMAGE_DIR
path to images
-od OUTPUT_DIR, --output_dir OUTPUT_DIR
path to output files
-a, --animate show animation
-np, --no-plot no plot is shown.
-q, --quiet minimalistic console output.
-i IGNORE [IGNORE ...], --ignore IGNORE [IGNORE ...]
ignore a list of classes.
--set-class-iou SET_CLASS_IOU [SET_CLASS_IOU ...]
set IoU for a specific class.
python evaluate_mAP_scores.py \
-pd input/detection-results \
-gt input/ground-truth \
-id input/images-optional/ \
-od ~/out/mAP/example
N.B.: including an image directory with -id is purely optional if you want to see the animation - in which case you will need the -a flag.
| Utility | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| convert_annotations | CLI & Library | Converts annotations styles depending on filetype for the purpose of mAP score calculation - simplified function call for the other utils modules. |
| convert_darkflow_json_to_pvoc_xml | CLI & Library | Converts darkflow style json annotations to Pascal VOC XML format. |
| convert_darkflow_json_to_xyxy_txt | CLI & Library | Converts xml annotations to space delimited file per image file with each row being an object in the format <left/xmin> <top/ymin> <right/xmax> <bottom/ymax>. |
| convert_pvoc_xml_to_darkflow_json | CLI & Library | Converts Pascal VOC XML files to Darkflow style json annotations |
| convert_pvoc_xml_to_xyxy_txt | CLI & Library | Converts darkflow style json annotations to space delimited file per image file with each row being an object in the format <left/xmin> <top/ymin> <right/xmax> <bottom/ymax>. |
| convert_pvoc_xml_to_yolo_lxywh_txt | CLI & Library | Converts darkflow style json annotations to space delimited file per image file with each row being an object in the format <norm_bbox_centre_x> <norm_bbox_centre_y> <norm_bbox_width> <norm_bbox_height>. |
Collection of python scripts that convert from different annotation formats to the format required for this tool. These are from the original repository and are not yet folded into the new library & CLI structure.
convert_gt_xml is an example of a script that has been moved from scripts/extra to utils after being refactored, and can be imported into other python scripts.
Consider this directory a "to do" list for conversion capabilities. At this stage there is no urgent intention to convert these other scripts - should there be a need feel free to convert it in the same manner and create a pull request.
N.B.: This explanation is from the original repository - authored by João Cartucho - I've left this as is because it's a fantastic explanation of mAP scores.
This code will evaluate the performance of your neural net for object recognition.
In practice, a higher mAP value indicates a better performance of your neural net, given your ground-truth and set of classes.
The performance of your neural net will be judged using the mAP criterium defined in the PASCAL VOC 2012 competition. We simply adapted the official Matlab code into Python (in our tests they both give the same results).
First (1.), we calculate the Average Precision (AP), for each of the classes present in the ground-truth. Finally (2.), we calculate the mAP (mean Average Precision) value.
For each class:
First, your neural net detection-results are sorted by decreasing confidence and are assigned to ground-truth objects. We have "a match" when they share the same label and an IoU >= 0.5 (Intersection over Union greater than 50%). This "match" is considered a true positive if that ground-truth object has not been already used (to avoid multiple detections of the same object).
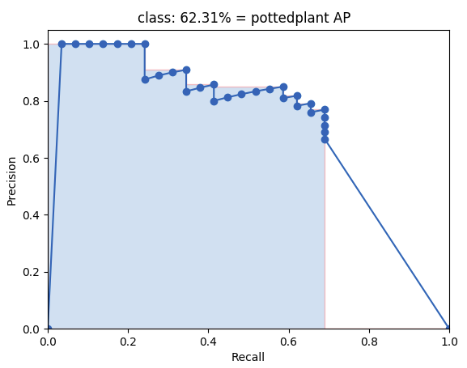
Using this criterium, we calculate the precision/recall curve. E.g:
Then we compute a version of the measured precision/recall curve with precision monotonically decreasing (shown in light red), by setting the precision for recall r to the maximum precision obtained for any recall r' > r.
Finally, we compute the AP as the area under this curve (shown in light blue) by numerical integration. No approximation is involved since the curve is piecewise constant.
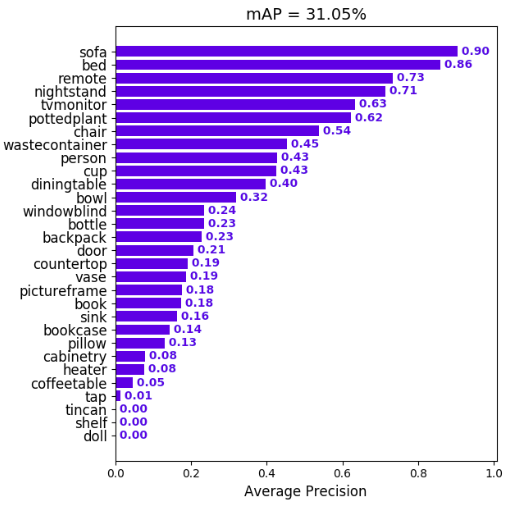
We calculate the mean of all the AP's, resulting in an mAP value from 0 to 100%. E.g:
This section is an excerpt from the original.
In the scripts/extra folder you can find additional scripts to convert PASCAL VOC, darkflow and YOLO files into the required format.
- Create a separate ground-truth text file for each image.
- Use matching names for the files (e.g. image: "image_1.jpg", ground-truth: "image_1.txt").
- In these files, each line should be in the following format:
<class_name> <left> <top> <right> <bottom> [<difficult>] - The
difficultparameter is optional, use it if you want the calculation to ignore a specific detection. - E.g. "image_1.txt":
tvmonitor 2 10 173 238 book 439 157 556 241 book 437 246 518 351 difficult pottedplant 272 190 316 259
- Create a separate detection-results text file for each image.
- Use matching names for the files (e.g. image: "image_1.jpg", detection-results: "image_1.txt").
- In these files, each line should be in the following format:
<class_name> <confidence> <left> <top> <right> <bottom> - E.g. "image_1.txt":
tvmonitor 0.471781 0 13 174 244 cup 0.414941 274 226 301 265 book 0.460851 429 219 528 247 chair 0.292345 0 199 88 436 book 0.269833 433 260 506 336