A high performance microservice framework for XGBoost models
Pre-Alpha. Working on finalizing API and optimizing performance. Subsequently, will create unit tests and documentation.
Most solutions for productionizing ML have separate deployment methods for real time model needs (e.g. an API or GRPC service, etc) vs batch scoring (e.g. some form of Spark or Dask based solution). This makes sense because methods that are optimized for one are generally not optimized for the other. Take a popular pattern at my employer as an example. They run their batch scoring by simply calling their API one row at a time a million times. This is nice because it's easy to set up, but what if your model takes a while to make its prediction? If you have a large amount of data, your batch process ends up being really slow unless you throw a large amount of parallelism/resources at it. To summarize, real time use cases need low latency, while batch processes need to take advantage of vectorization to process through large volumes of data quickly. Enter XGBatch.
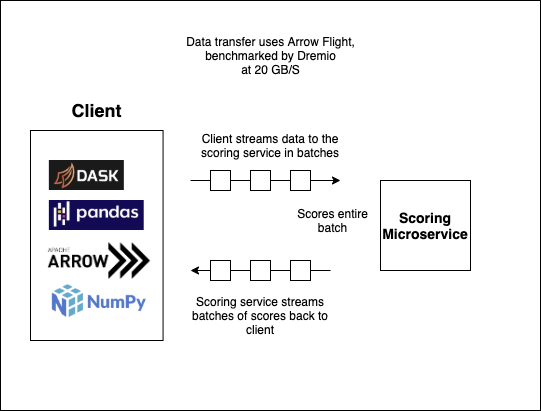
XGBATCH uses Apache Arrow's Flight framework (which uses GRPC under the hood) to stream batches of data to the scoring service, which it then scores as a batch (allowing it to reap the fruits of vectorization), and finally streams the batch back to the client. Using Flight gives us low latency for real time use cases, as well as an efficient method for scoring large batches of data.
First, install the python package.
pip3 install xgbatch
Next, we'll start the scoring service. We'll assume you have a pre-trained xgboost model called 'model.model'.
from xgbatch import serve_xgb_batch
serve_xgb_batch("127.0.0.1", "8989", "model.model")
This command will start a scoring service listening on the loopback interface on port 8989.
Now, in different terminal, load a dataframe and send it to get scored.
import pandas as pd
from xgbatch import score_pandas
df = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
result = score_pandas(df, "127.0.0.1", "8989")
Or for a 2d numpy array (in the same format you'd usually pass to xgboost):
from xgbatch import score_numpy
arr = load_my_np_array()
result = score_numpy(arr, "127.0.0.1", "8989")
With dask:
import dask.dataframe as dd
from xgbatch import score_pandas
ddf = dd.read_csv('data.csv')
ddf = ddf.map_partitions(lambda df: score_pandas(df, "127.0.0.1", "8989"))
df = ddf.compute()
There are basic integration tests to ensure the client apis are working for all the different client types. The tests use a pretrained model against saved data from the iris dataset to ensure we are getting repeatable results.
Activate the virtual environment:
source env/bin/activate
Install the necessary packages:
pip3 install -r requirements-test.txt
Run the tests:
pytests integration/