-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 126
/
Copy pathL0230_KthSmallestElementInBST.java
81 lines (70 loc) · 2.49 KB
/
L0230_KthSmallestElementInBST.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
import common.TreeNode;
/**
* https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
*
* 给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
*
* 示例 1:
* 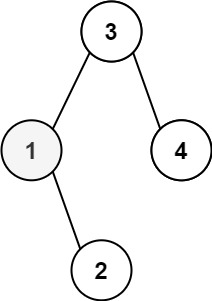
* 输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
* 输出:1
*
* 示例 2:
* 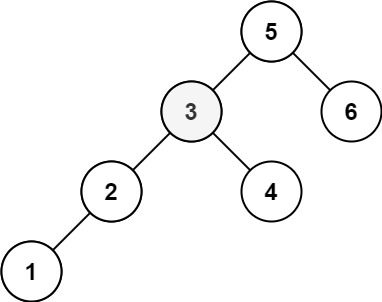
* 输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
* 输出:3
*
* 提示:
* - 树中的节点数为 n
* - 1 <= k <= n <= 10⁴
* - 0 <= Node.val <= 10⁴
*
* 进阶:如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化算法?
*/
public class L0230_KthSmallestElementInBST {
private int count = 0; // 记录当前访问的节点数
private int result = 0; // 记录第 k 小的元素
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inorder(root, k);
return result;
}
/**
* 中序遍历二叉搜索树
* 由于二叉搜索树的中序遍历是递增序列,所以第 k 个访问的节点就是第 k 小的元素
*/
private void inorder(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null || count >= k) {
return;
}
// 遍历左子树
inorder(node.left, k);
// 处理当前节点
count++;
if (count == k) {
result = node.val;
return;
}
// 遍历右子树
inorder(node.right, k);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
L0230_KthSmallestElementInBST solution = new L0230_KthSmallestElementInBST();
// 测试用例 1
TreeNode root1 = new TreeNode(3);
root1.left = new TreeNode(1);
root1.right = new TreeNode(4);
root1.left.right = new TreeNode(2);
System.out.println(solution.kthSmallest(root1, 1)); // 应输出:1
// 重置计数器
solution.count = 0;
solution.result = 0;
// 测试用例 2
TreeNode root2 = new TreeNode(5);
root2.left = new TreeNode(3);
root2.right = new TreeNode(6);
root2.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
root2.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
root2.left.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
System.out.println(solution.kthSmallest(root2, 3)); // 应输出:3
}
}