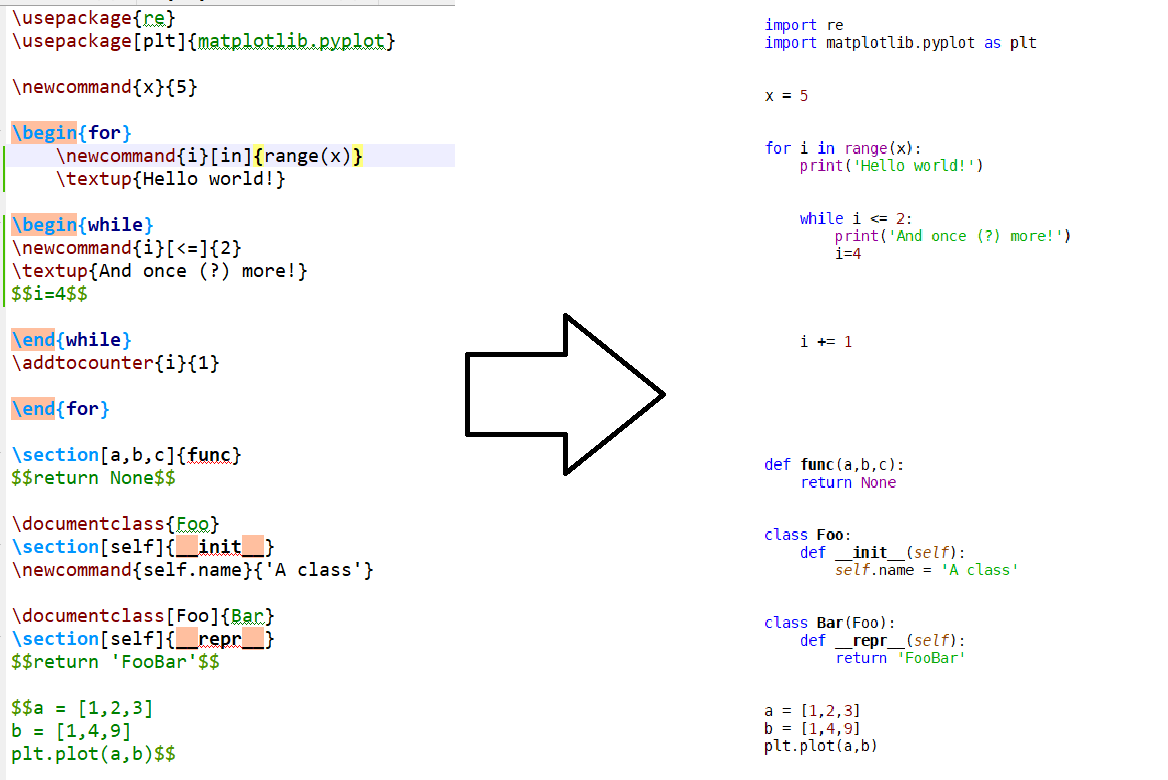
| Python | LaTeX.py equivalent |
|---|---|
import <module> |
\usepackage{<module>} |
import <module> as <name> |
\usepackage[<name>]{<module>} |
print(<value>) |
\textup(<value>) |
<variable_name> = <value> |
\newcommand{<variable_name>}{<value> } |
<variable_name> += <value> |
\addtocounter{<variable_name>}{<value>} |
for (<variable><operator><value>): |
\begin{for} |
\newcommand{<variable>}[<operator>]{<value>} |
|
\end{for} |
|
while (<variable><operator><value>): |
\begin{while} |
\newcommand{<variable>}[<operator>]{<value>} |
|
\end{while} |
|
class <name>: |
\documentclass{<name>} |
class <name>(<parent>): |
\documentclass[<parent>]{<name>} |
def <name>(<parameters>): |
\section[<parameters>]{<name>} |
l = LaTeX(<filename>)- filename: Name of the .tex file to be translated
l.parse_file()l.execute()l.save(filename=<filename>)- filename: Optional. Name of the .py file to save the
exec_stringto. If not provided, the latter is saved to a file with the same name as the original .tex file, but different extension.