算法(Algorithm)是指解题方案的准确而完整的描述,是一系列解决问题的清晰指令,算法代表着用系统的方法描述解决问题的策略机制。也就是说,能够对一定规范的输入,在有限时间内获得所要求的输出。如果一个算法有缺陷,或不适合于某个问题,执行这个算法将不会解决这个问题。不同的算法可能用不同的时间、空间或效率来完成同样的任务。一个算法的优劣可以用空间复杂度与时间复杂度来衡量。
- 有穷性
算法的有穷性是指算法必须能在执行有限个步骤之后终止;
- 确定性
算法的每一步骤必须有确切的定义;
- 输入
一个算法有0个或多个输入
- 输出
一个算法有一个或多个输出,以反映对输入数据加工后的结果
- 可行性
算法中执行的任何计算步骤都是可以被分解为基本的可执行的操作步
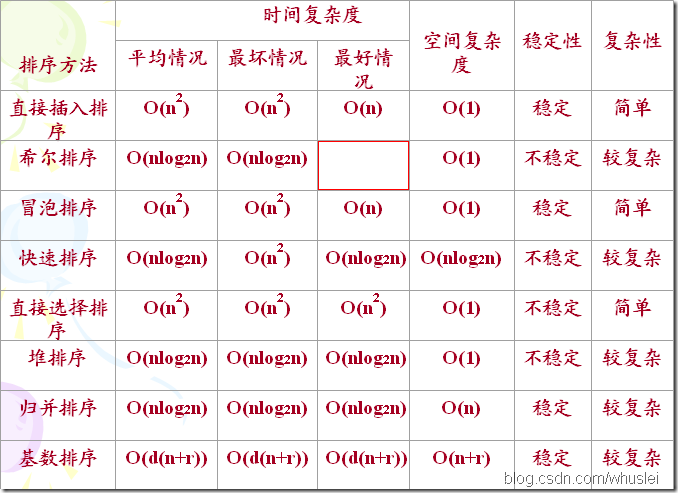
时间复杂度是执行算法所需要的工作量,一般来说,计算机算法是问题规模n 的函数f(n),算法的时间复杂度也因此记做。
T(n)=Ο(f(n))
因此,问题的规模n 越大,算法执行的时间的增长率与f(n) 的增长率正相关
算法的空间复杂度是指算法需要消耗的内存空间。其计算和表示方法与时间 复杂度类似。
function BubbleSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($j = 1; $j < $count; $j++) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $count - $j; $i++) {
if ($container[$i] > $container[$i + 1]) {
$temp = $container[$i];
$container[$i] = $container[$i + 1];
$container[$i + 1] = $temp;
}
}
}
return $container;
}function InsertSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++){
$temp = $container[$i];
$j = $i - 1;
// Init
while($j >= 0 && $container[$j] > $temp){
$container[$j+1] = $container[$j];
$j--;
}
if($i != $j+1)
$container[$j+1] = $temp;
}
return $container;
}function ShellSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($increment = intval($count / 2); $increment > 0; $increment = intval($increment / 2)) {
for ($i = $increment; $i < $count; $i++) {
$temp = $container[$i];
for ($j = $i; $j >= $increment; $j -= $increment) {
if ($temp < $container[$j - $increment]) {
$container[$j] = $container[$j - $increment];
} else {
break;
}
}
$container[$j] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}function SelectSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 0; $i < $count; $i++){
$k = $i;
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $count; $j++){
if($container[$j] < $container[$k]){
$k = $j;
}
}
if($k != $i){
$temp = $container[$i];
$container[$i] = $container[$k];
$container[$k] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}function QuickSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
if ($count <= 1) { // 基线条件为空或者只包含一个元素,只需要原样返回数组
return $container;
}
$pivot = $container[0]; // 基准值 pivot
$left = $right = [];
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
if ($container[$i] < $pivot) {
$left[] = $container[$i];
} else {
$right[] = $container[$i];
}
}
$left = QuickSort($left);
$right = QuickSort($right);
return array_merge($left, [$container[0]], $right);
}- 归并排序
- 堆排序
- 顺序查找
function find($array ,$target) {
foreach ($array as $key=>$value) {
if($value === $target) {
return key;
}
}
return false;
}- 有序查找(二分查找)
function BinaryQueryRecursive(array $container, $search, $low = 0, $top = 'default')
{
$top == 'default' && $top = count($container);
if ($low <= $top) {
$mid = intval(floor($low + $top) / 2);
if (!isset($container[$mid])) {
return false;
}
if ($container[$mid] == $search) {
return $mid;
}
if ($container[$mid] < $search) {
return BinaryQueryRecursive($container, $search, $mid + 1, $top);
} else {
return BinaryQueryRecursive($container, $search, $low, $mid - 1);
}
}
}- 动态查找(BST)
- 哈希表 O(1)
- 迭代
- 递归
- 动态规划
- 回溯
- 分治
- 贪心
-
字符串
- 查找字符串中的字符
- 翻转字符串
-
排序
- 冒泡排序
- 快速排序
- 归并排序
-
链表
- 翻转链表
- 链表有没有环
-
二叉搜索树
- 二叉树的深度
- 二叉树的遍历
- 重建二叉树